SAS 9.4 Programming Fundamentals A00-215 Exam Practice Test
Which line contains a syntax error?

Answer : A
In the provided code snippet, Line 3 contains a syntax error. The keep statement is used incorrectly here; the correct keyword to use is where in order to filter the dataset. The correct line should be something like:
where Make = 'Honda';
So, the keep statement on Line 3 is not properly used, and also there appears to be a missing quotation mark at the end of 'Honda' which should be closed before the semicolon.
SAS documentation for the where statement.
Fill in blank
What is the default byte size of a numeric variable?
Thedefault lengthofnumeric variablesin SAS data sets is ______bytes
Enter your numeric answer in the space above.
Answer : A
Thedefault lengthofnumeric variablesin SAS data sets is 8bytes.
In SAS, the default byte size of a numeric variable is 8 bytes. This allows for a significant amount of precision and a wide range of numeric values to be stored within a numeric variable, regardless of the actual number of digits in the number being stored.
SAS documentation on numeric variables, SAS Institute.
The following program is summited:

The following report is created:
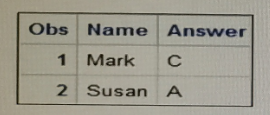
However, the desired report is shown below:
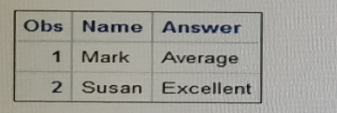
What change is needed to display the desired formatted values for the Answer varia
Answer : C
When defining custom formats in SAS, it's important to adhere to the correct syntax, which includes ending format names with a period. In the submitted program, the format $convert is defined without a period at the end of the format name in the VALUE statement. This is likely causing an error since format names in the VALUE statement should always end with a period. Option C correctly identifies that adding a period to the end of the format name on the VALUE statement will allow SAS to properly recognize and apply the custom format to the Answer variable when the PROC PRINT step is executed.
The program provided in the question seems to have formatting errors, but based on the information provided, the suggested change is to add a period to make it $convert. which would correctly apply the format.
The other options would not resolve the issue of applying the custom format:
A . Changing the case of the unformatted values will not help if the format is not correctly specified.
B . The comma does not seem to be the issue based on the context given.
D . The dollar sign is correct and necessary for character formats; removing it would cause the format to be invalid for character data.
SAS 9.4 documentation for the FORMAT procedure: SAS Help Center: PROC FORMAT
Given the data set NAMES:
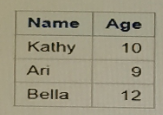
Which PROC SORT program creates the NAMES data set shown below?

Answer : A
The PROC SORT step in SAS is used to sort data sets by one or more variables. The syntax for the proc sort step requires the by statement to specify the variable(s) by which to sort the data. The correct answer is option A:
proc sort data=Names;
by Name;
run;
This sorts the data set by the variable 'Name' in alphabetical order, which matches the sorted NAMES data set shown in the question. Option B uses orderby, which is not a valid SAS statement. Option C sorts by 'Age', which would not give the same result as shown in the question. Option D also incorrectly uses orderby.
Which program assigns the library reference exlib to the CLASS. XLSX workbook and displays the CLASS_TEST worksheet?
Answer : D
The correct answer is option D, which uses the LIBNAME statement correctly to assign a library reference to an Excel workbook and specifies the correct syntax for accessing a worksheet within that workbook. The syntax for this option is:
libname exlib xlsx 'c:\class.xlsx';
proc print data=exlib.class_test;
run;
This code snippet assigns the library reference exlib to the Excel workbook located at c:\class.xlsx using the XLSX engine. The PROC PRINT step is then used to display the contents of the worksheet named CLASS_TEST within that workbook. The library reference exlib combined with the dataset name class_test (following the .) correctly specifies the worksheet to be printed. The other options (A, B, C) are incorrect due to various reasons: incorrect syntax for the LIBNAME statement, incorrect specification of the dataset to be printed, and incorrect path specifications. Reference: SAS 9.4 Guide to Software Updates.
Which statement is true about the SUM statement?
Answer : C
The SUM statement in SAS is used to sum values across observations, adding the value of the expression on the right side of the statement to the variable on the left. It does not use an equal sign (eliminating A), only one variable can be on the left-hand side of a SUM statement (eliminating B), and it is not initialized to 1 by default (eliminating D). What makes the SUM statement particularly useful is that it ignores missing values when summing across observations, which means that missing values do not affect the sum (option C is correct).
SAS documentation on the SUM statement, SAS Institute.
Which PROC MEANS statements specifies variables to group the data before calculating statistics?
Answer : A
In the context of the PROC MEANS procedure in SAS, the CLASS statement is used to specify categorical variables whose unique values group the data before calculating statistics. This allows PROC MEANS to calculate statistics like the mean, sum, or standard deviation for each class or group of data defined by the CLASS variables.
The CLASS statement works as follows:
class variable-list; specifies one or more variables to define groups for analysis.
When used, PROC MEANS computes the requested statistics for each level of the variables listed, which can be very helpful for analyzing how groups compare across different statistics.
The other options are not used in the PROC MEANS procedure to specify grouping of data:
B . GROUP is not a valid statement in PROC MEANS.
C . SUMBY is not a valid statement in SAS.
D . VAR is used in PROC MEANS to specify the analysis variables for which statistics are to be computed, not to group the data.