Snowflake SnowPro Advanced: Architect Certification ARA-C01 Exam Practice Test
Which system functions does Snowflake provide to monitor clustering information within a table (Choose two.)
Answer : A, C
According to the Snowflake documentation, these two system functions are provided by Snowflake to monitor clustering information within a table. A system function is a type of function that allows executing actions or returning information about the system. A clustering key is a feature that allows organizing data across micro-partitions based on one or more columns in the table. Clustering can improve query performance by reducing the number of files to scan.
Based on the architecture in the image, how can the data from DB1 be copied into TBL2? (Select TWO).
A)

B)

C)

D)
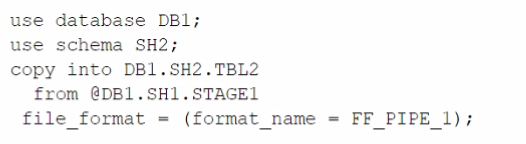
E)

Answer : B, E
The architecture in the image shows a Snowflake data platform with two databases, DB1 and DB2, and two schemas, SH1 and SH2. DB1 contains a table TBL1 and a stage STAGE1. DB2 contains a table TBL2. The image also shows a snippet of code written in SQL language that copies data from STAGE1 to TBL2 using a file format FF PIPE 1.
To copy data from DB1 to TBL2, there are two possible options among the choices given:
SQLAI-generated code. Review and use carefully.More info on FAQ.
use database DB2;
use schema SH2;
create stage EXT_STAGE1
url = @DB1.SH1.STAGE1;
SQLAI-generated code. Review and use carefully.More info on FAQ.
copy into TBL2
from @EXT_STAGE1
file format = (format name = DB1.SH1.FF PIPE 1);
SQLAI-generated code. Review and use carefully.More info on FAQ.
use database DB2;
use schema SH2;
insert into TBL2
select * from DB1.SH1.TBL1;
The other options are not valid because:
1: CREATE STAGE | Snowflake Documentation
A group of Data Analysts have been granted the role analyst role. They need a Snowflake database where they can create and modify tables, views, and other objects to load with their own data. The Analysts should not have the ability to give other Snowflake users outside of their role access to this data.
How should these requirements be met?
Answer : C
The requirements state that the data analysts need to be able to create and modify database objects and load data, but should not be able to manage access for users outside of their role.
Option C: By making each schema within the database a managed access schema and having them owned by SYSADMIN, the ability to grant privileges on the schema's objects is strictly controlled. Managed access schemas limit the granting of privileges to the role specified as the owner of the schema, in this case, SYSADMIN. The ANALYST_ROLE can be granted the privileges necessary to create and modify objects within these schemas, satisfying the requirement for the analysts to perform their tasks without being able to extend access beyond their role.
An Architect has chosen to separate their Snowflake Production and QA environments using two separate Snowflake accounts.
The QA account is intended to run and test changes on data and database objects before pushing those changes to the Production account. It is a requirement that all database objects and data in the QA account need to be an exact copy of the database objects, including privileges and data in the Production account on at least a nightly basis.
Which is the LEAST complex approach to use to populate the QA account with the Production account's data and database objects on a nightly basis?
Answer : C
This approach is the least complex because it uses Snowflake's built-in replication feature to copy the data and database objects from the Production account to the QA account. Replication is a fast and efficient way to synchronize data across accounts, regions, and cloud platforms. It also preserves the privileges and metadata of the replicated objects. By creating clones of the replica databases, the QA account can run tests on the cloned data without affecting the original data. Clones are also zero-copy, meaning they do not consume any additional storage space unless the data is modified. This approach does not require any external stages, tasks, Snowpipe, or external functions, which can add complexity and overhead to the data transfer process.
Introduction to Replication and Failover
How can an Architect enable optimal clustering to enhance performance for different access paths on a given table?
Answer : B
According to the SnowPro Advanced: Architect documents and learning resources, the best way to enable optimal clustering to enhance performance for different access paths on a given table is to create multiple materialized views with different cluster keys. A materialized view is a pre-computed result set that is derived from a query on one or more base tables. A materialized view can be clustered by specifying a clustering key, which is a subset of columns or expressions that determines how the data in the materialized view is co-located in micro-partitions. By creating multiple materialized views with different cluster keys, an Architect can optimize the performance of queries that use different access paths on the same base table. For example, if a base table has columns A, B, C, and D, and there are queries that filter on A and B, or on C and D, or on A and C, the Architect can create three materialized views, each with a different cluster key: (A, B), (C, D), and (A, C). This way, each query can leverage the optimal clustering of the corresponding materialized view and achieve faster scan efficiency and better compression.
Snowflake Documentation: Materialized Views
Snowflake Learning: Materialized Views
A company wants to Integrate its main enterprise identity provider with federated authentication with Snowflake.
The authentication integration has been configured and roles have been created in Snowflake. However, the users are not automatically appearing in Snowflake when created and their group membership is not reflected in their assigned rotes.
How can the missing functionality be enabled with the LEAST amount of operational overhead?
Answer : D
The best way to integrate an enterprise identity provider with federated authentication and enable automatic user creation and role assignment in Snowflake is to use SCIM (System for Cross-domain Identity Management). SCIM allows Snowflake to synchronize with the identity provider and create users and groups based on the information provided by the identity provider. The groups are mapped to roles in Snowflake, and the users are assigned the roles based on their group membership. This way, the identity provider remains the source of truth for user and group management, and Snowflake automatically reflects the changes without manual intervention. The other options are either incorrect or incomplete, as they involve using OAuth, which is a protocol for authorization, not authentication or user provisioning, and require additional configuration of authorization and resource servers.
An Architect needs to design a Snowflake account and database strategy to store and analyze large amounts of structured and semi-structured data. There are many business units and departments within the company. The requirements are scalability, security, and cost efficiency.
What design should be used?
Answer : D
The best design to store and analyze large amounts of structured and semi-structured data for different business units and departments is to use a centralized Snowflake database for core business data, and use separate databases for departmental or project-specific data. This design allows for scalability, security, and cost efficiency by leveraging Snowflake's features such as:
Database cloning:Cloning a database creates a zero-copy clone that shares the same data files as the original database, but can be modified independently. This reduces storage costs and enables fast and consistent data replication for different purposes.
Database sharing:Sharing a database allows granting secure and governed access to a subset of data in a database to other Snowflake accounts or consumers. This enables data collaboration and monetization across different business units or external partners.