WGU Data Management - Foundations Exam Practice Test
Which statement is associated with two separate entities?
Answer : C
A relationship in an ER model defines how two separate entities interact.
Example Usage:
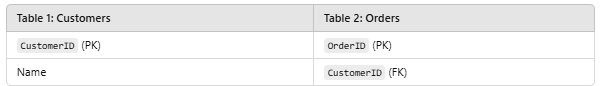
CREATE TABLE Customers (
CustomerID INT PRIMARY KEY,
Name VARCHAR(50)
);
CREATE TABLE Orders (
OrderID INT PRIMARY KEY,
CustomerID INT,
FOREIGN KEY (CustomerID) REFERENCES Customers(CustomerID)
);
Customers and Orders are separate entities, related via CustomerID.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
Option A (Reflexive relationship) (Incorrect): Used for self-referencing entities, not two different entities.
Option B (Entity type) (Incorrect): Defines a class of objects, but does not establish relationships.
Option D (Attribute) (Incorrect): Attributes describe entities but do not connect them.
Thus, the correct answer is Relationship, as it connects two separate entities.
Which optional clause is used to reject inserts and updates that do not satisfy the WHERE clause of a view query?
Answer : A
When a VIEW is created in SQL, users may insert or update data through that view. However, if a row is inserted or updated in such a way that it violates the condition of the VIEW's WHERE clause, it can lead to inconsistencies.
To prevent such unwanted modifications, SQL provides the WITH CHECK OPTION clause.
How WITH CHECK OPTION Works:
Ensures that any new data (INSERT/UPDATE) still fits within the defined constraints of the VIEW.
If a user tries to insert or update a row that would not appear in the VIEW, the operation is rejected.
Example:
sql
CREATE VIEW HighSalaryEmployees AS
SELECT * FROM Employees WHERE Salary > 50000
WITH CHECK OPTION;
Now, if someone attempts:
sql
INSERT INTO HighSalaryEmployees (ID, Name, Salary)
VALUES (101, 'Alice', 30000);
This fails because 30000 does not satisfy Salary > 50000.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
Option B (Incorrect): JOIN VIEWS is not a valid SQL clause.
Option C (Incorrect): MATERIALIZED VIEW refers to stored views in some databases, but it does not reject incorrect inserts/updates.
Option D (Incorrect): BASE TABLE refers to the original table from which a VIEW is created.
Thus, the correct answer is WITH CHECK OPTION, which ensures that only valid data modifications occur.
Which expression can be used to create a temporary name for a table?
Answer : C
An alias is used in SQL to give a temporary name to a table or column within a query. It makes queries more readable and helps in cases where a table needs to be referenced multiple times (e.g., in a self-join).
Example Usage:
sql
SELECT e.Name, d.DepartmentName
FROM Employees AS e
JOIN Departments AS d
ON e.DeptID = d.ID;
Here, Employees is aliased as e and Departments as d, making the query shorter and clearer.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
Option A (HAVING) (Incorrect): Used to filter grouped results, not create aliases.
Option B (NEW) (Incorrect): Not a valid SQL keyword for aliasing.
Option D (UNION) (Incorrect): Combines result sets but does not rename tables.
Thus, the correct answer is ALIAS, which allows for temporary naming of tables or columns.
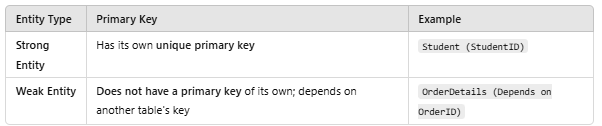
Which main characteristic is used to differentiate between strong and weak entities in the process of database design?
Answer : B
In database design, an entity is classified as strong or weak based on whether it has a primary key that uniquely identifies its records.
Differences Between Strong and Weak Entities:
CREATE TABLE Orders (
OrderID INT PRIMARY KEY,
CustomerID INT
);
CREATE TABLE OrderDetails (
OrderDetailID INT,
OrderID INT,
ProductID INT,
PRIMARY KEY (OrderDetailID, OrderID),
FOREIGN KEY (OrderID) REFERENCES Orders(OrderID)
);
Orders is a strong entity (has OrderID as its own primary key).
OrderDetails is a weak entity (depends on OrderID for uniqueness).
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
Option A (Association) (Incorrect): Associations describe relationships but do not define strong/weak entities.
Option C (Foreign key) (Incorrect): Weak entities depend on foreign keys, but primary keys define their status.
Option D (Cardinality) (Incorrect): Cardinality defines relationship constraints but does not differentiate entity types.
Thus, the correct answer is Primary key, as it is the defining characteristic between strong and weak entities.
Which clause from a SELECT statement immediately accompanies the SELECT clause in MySQL?
Answer : A
In SQL syntax, the FROM clause is the first clause that follows SELECT. It specifies the table(s) from which the data will be retrieved.
Example:
sql
SELECT name, salary FROM Employees;
Option A (Correct): The FROM clause immediately follows the SELECT clause in MySQL.
Option B (Incorrect): VALUE is not a valid clause in MySQL SELECT statements.
Option C (Incorrect): WHERE is used to filter records after specifying the table in FROM.
Option D (Incorrect): TABLE is not a valid clause following SELECT in SQL.
Which statement uses valid syntax for the DELETE statement in SQL?
Answer : B
The correct syntax for deleting records from a table in SQL is:
sql
DELETE FROM table_name WHERE condition;
This deletes only the rows that match the condition.
Example Usage:
sql
DELETE FROM Employees WHERE Salary < 30000;
Deletes all employees earning less than $30,000.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
Option A (Incorrect): Missing FROM keyword. The correct syntax is DELETE FROM table_name.
Option C (Partially Correct): DELETE FROM table_name; deletes all rows, but it lacks a WHERE clause.
Option D (Incorrect): DELETE * is not valid in SQL. The correct command is just DELETE FROM.
Thus, the correct answer is DELETE FROM table_name WHERE condition;.
What is the role of the transaction manager within the database system architecture?
Answer : C
A Transaction Manager ensures ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) properties in database transactions. It manages concurrent transactions, ensuring no conflicts occur and logs modifications to support recovery mechanisms.
Option A (Incorrect): Query optimization is managed by the query processor, not the transaction manager.
Option B (Incorrect): The transaction manager is a component of the database architecture but is not composed of the entire system (query processor, storage manager, etc.).
Option C (Correct): The transaction manager logs transactions like INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE, ensuring consistency and recoverability.
Option D (Incorrect): The storage manager is responsible for translating queries into file system commands.