WGU Integrated Physical Sciences (MTC1) WGU (MTC1) Integrated Physical Sciences Exam Practice Test
Which question would be appropriate for an observational study?
Answer : B
An observational study involves collecting data without manipulating any variables. The question 'What is the brightest star that can be seen from Earth?' fits this criteria as it involves observing and recording data about stars without any experimental intervention. Other options involve controlled experiments where variables are manipulated. Reference:
Integrated Physical Sciences, Chapter 2: Methods of Scientific Investigation
In which scenario is gravity the force that causes the object's change in motion?
Answer : D
Gravity is the force responsible for the motion of a ball falling from a shelf to the floor. As the ball is released, gravity pulls it downward, causing it to accelerate towards the floor. Reference:
Integrated Physical Sciences, Chapter 3: Forces and Motion
Which statement describes the relationship between mass and acceleration when the net force on an object is kept constant?
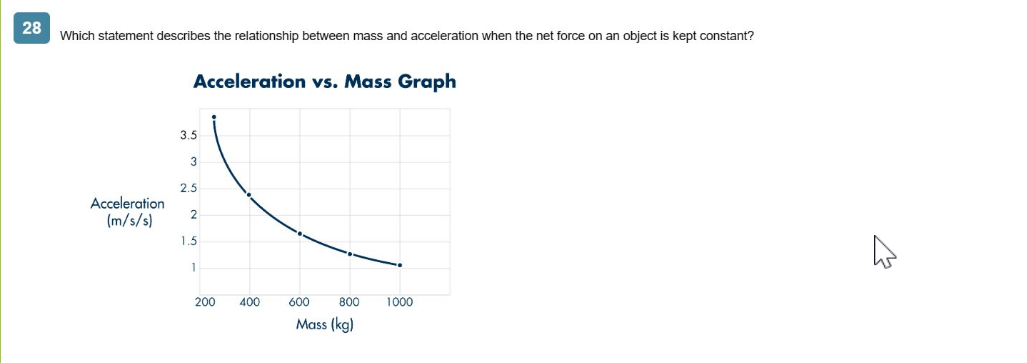
Answer : B
1. **Understanding the Graph**: The graph provided shows the relationship between acceleration (in m/s) and mass (in kg). The x-axis represents mass, and the y-axis represents acceleration. 2. **Observing the Trend**: The graph shows a decreasing curve, which indicates that as the mass increases, the acceleration decreases. 3. **Newton's Second Law of Motion**: According to Newton's Second Law of Motion, \( F = ma \), where \( F \) is the force, \( m \) is the mass, and \( a \) is the acceleration. If the net force (\( F \)) is kept constant, then \( a = \frac{F}{m} \). 4. **Inverse Proportionality**: The equation \( a = \frac{F}{m} \) suggests that acceleration \( a \) is inversely proportional to the mass \( m \). This means that if the mass increases, the acceleration decreases proportionally. 5. **Conclusion**: Based on the graph and Newton's Second Law, the correct description of the relationship is that mass and acceleration are inversely proportional. **Reference**: - Newton's Second Law of Motion: Basic principle in physics indicating the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration.
Hail falls into the ocean.
Between which two reservoirs is the hail transferred during this process?
Answer : C
Hail is a form of solid precipitation that originates in the atmosphere. When hail falls into the ocean, it is transferred from the atmosphere (where it formed) to the surface water reservoir (the ocean). This process is part of the hydrological cycle, which involves the movement of water between different reservoirs, including the atmosphere, surface water, ground water, and glaciers.
Integrated Physical Sciences materials on precipitation and the hydrological cycle.
Studies on the movement of water between atmospheric and surface water reservoirs.
Consider the location of nitrogen (N) on the periodic table
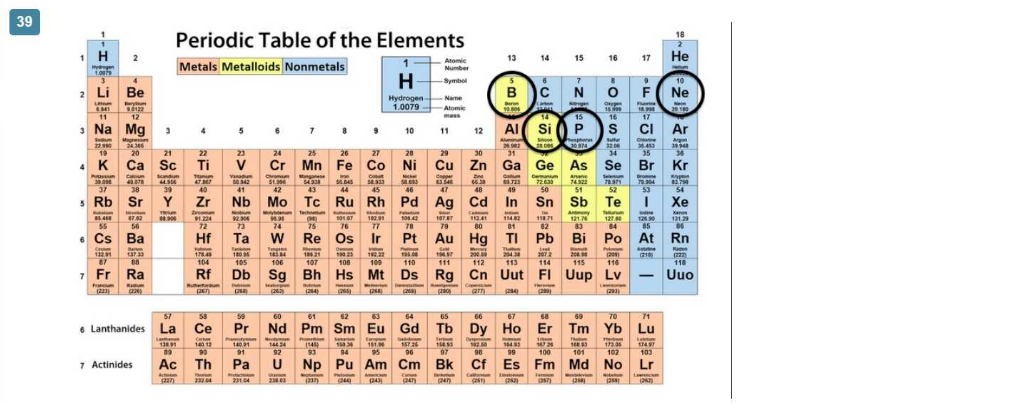
Which element has chemical properties that are similar to nitrogen's7
Answer : B
Elements in the same group (column) of the periodic table have similar chemical properties because they have the same number of valence electrons. Phosphorus (P) is in the same group as nitrogen (N), Group 15, and thus has similar chemical properties. In comparison:
Neon (Ne) is a noble gas in Group 18.
Silicon (Si) is in Group 14.
Boron (B) is in Group 13.
Integrated Physical Sciences Learning Resources, Chapter on the Periodic Table
Which location has high risk of earthquakes but low risk of volcanic activity?
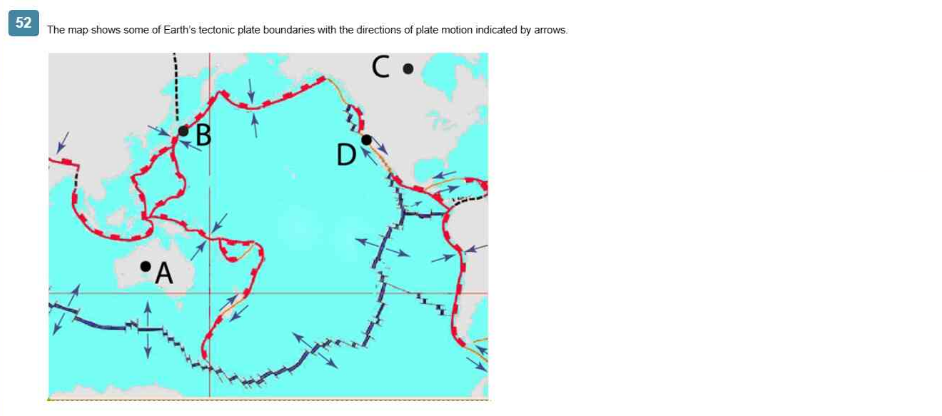
Answer : B
Location B on the map corresponds to a region along the San Andreas Fault in California, which is a transform plate boundary. At transform boundaries, plates slide past each other horizontally. This movement can cause significant stress accumulation and release in the form of earthquakes. However, this type of boundary does not typically produce volcanic activity, which is more common at divergent and convergent boundaries. Therefore, location B has a high risk of earthquakes but a low risk of volcanic activity.
Integrated Physical Sciences resources on tectonic plate boundaries.
Studies on the San Andreas Fault and seismic activity.
Which type of wave travels the slowest?
Answer : D
1. **Wave Speeds**: The speed of different types of waves varies significantly. 2. **Gamma Waves**: These are electromagnetic waves that travel at the speed of light (approximately \( 3 \times 10^8 \) m/s). 3. **Radio Waves**: Another type of electromagnetic wave, also traveling at the speed of light. 4. **Visible Light Waves**: These are also electromagnetic waves traveling at the speed of light. 5. **Sound Waves**: Travel much slower compared to electromagnetic waves, with typical speeds in air around 343 m/s. 6. **Conclusion**: Among the given options, sound waves travel the slowest. **Reference**: - Wave Speed Comparisons: Differences in propagation speeds of sound and electromagnetic waves.